author: @Demian
references: https://learn.0xparc.org/materials/halo2
Fibonacci Example 2
回顾 Example-1 里的 Table:
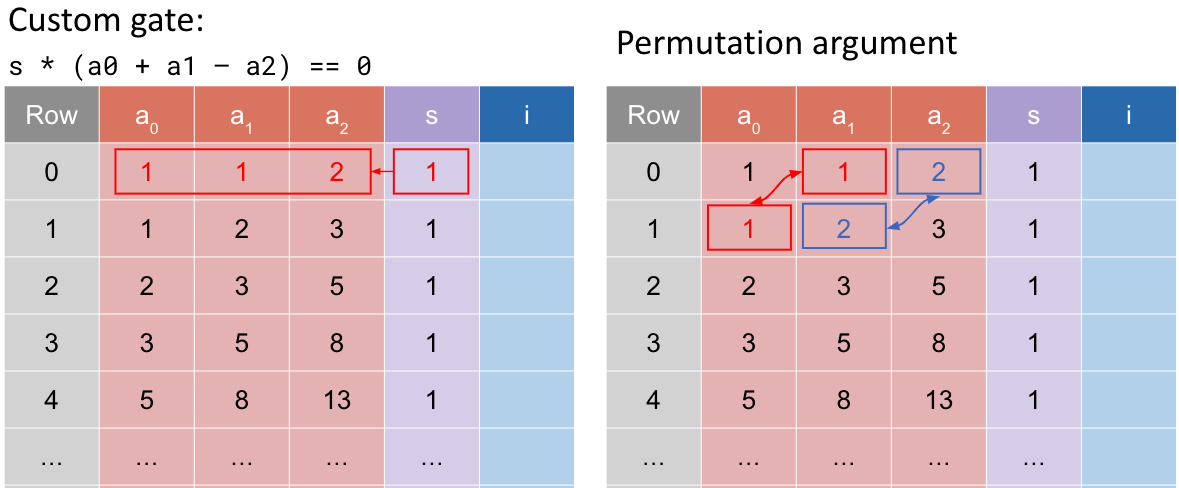
在 example-1 中有一些问题:
- 重复单元格太多,每次需要将 2 个单元格从上一行复制到下一行,效率不高
- 更好的解决方案:使用 Rotation 来访问多行是个更好的方案
如下图:
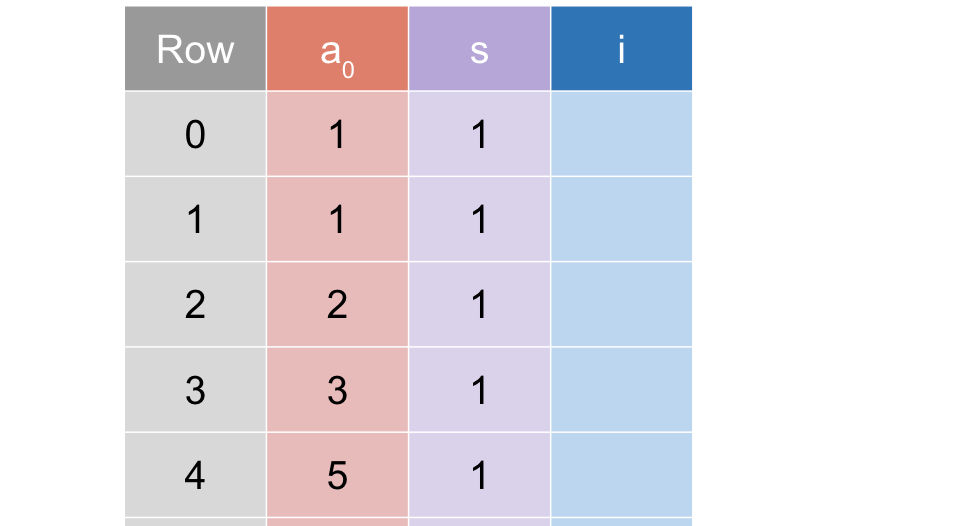
Overview
在本例子中, 代码将更加紧凑和模块化, 以下是一些主要的区别 :
Advice Columns:
- ex 1 :
- 用了 3 个 advice columns:
col_a,col_b和col_c,表的的第一行用来存储 Fibonacci 序列的连续的 3 个数
- 用了 3 个 advice columns:
- ex 2:
- 仅使用了一个 advice column,并依赖 Rotation(轮转, 即 )来访问连续的行,减少了各种复制
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { // example-1 pub fn configure(.., advice: [Column<Advice>; 3], ..) { let col_i = advice[ii]; meta.enable_equality(col_i); // 很多列需要声明 和 需要 enable... meta.create_gate("add", |meta| { let s = meta.query_selector(selector); let a = meta.query_advice(col_a, Rotation::cur()); //📢 let b = meta.query_advice(col_b, Rotation::cur()); //📢 let c = meta.query_advice(col_c, Rotation::cur()); //📢 vec![s * (a + b - c)] } ---------------------------------------- // example-2 pub fn configure(.., advice: Column<Advice>, ..) { let col_i = advice[ii]; meta.enable_equality(advice); meta.enable_equality(instance); // Gen Custom Gate: meta.create_gate("add", |meta| { // // advice | selector // a | s // b | // c | // let s = meta.query_selector(selector); let a = meta.query_advice(advice, Rotation::cur()); let b = meta.query_advice(advice, Rotation::next()); let c = meta.query_advice(advice, Rotation(2)); vec![s * (a + b - c)] }); }
Rotation::cur()当前行Rotation::next()下一行Rotation(2)再下一行
The Polynomial Identity:
数据赋值:
- ex 1: 初始的 Fibonacci 数
a和b被赋值到两个不同的 advice columns,而他们的和则被赋值到第三个 column。 - ex 2: 所有的 Fibonacci 数都在同一个 advice column,但在不同的行 (thanks to rotation)
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { //// Example 2 //// pub fn assign( &self, mut layouter: impl Layouter<F>, nrows: usize, // 前 2 列赋值之后, 后面要搞的列数.. ) -> Result<ACell<F>, Error> { layouter.assign_region( || "entire fibonacci table", |mut region| { // 为前两行启用 selector, 这意味着我们将从 instance (public input) 列中复制 Fibo 序列的前 2 个数字 self.config.selector.enable(&mut region, 0)?; self.config.selector.enable(&mut region, 1)?; // assign_advice_from_instance 方法,将 instance (public input) 列的前 2 个值 // (即 Fibonacci 序列的前两个数字)赋给 advice 列中的前 2 个单元格 // 后面在 MockProver 中, 我们会传入 instance 作为 Public input let mut a_cell = region.assign_advice_from_instance( || "1", self.config.instance, 0, // instance column's row 0 self.config.advice, 0, // 复制到当前的 region 的 row 0 ).map(ACell)?; let mut b_cell = region.assign_advice_from_instance( || "1", self.config.instance, 1, // instance column's row 1 self.config.advice, 1, // 复制到当前的 region 的 row 1 ).map(ACell)?; /// ..... }, ) } }
生成的 Fibonacci 数:
- ex 1: 使用方法
assign_row从前两个数生成下一个数。 - ex 2: 使用一个循环在整个 Fibonacci 表格中为所有的数赋值。
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { //// Example 2 //// pub fn assign(..., nrows){ /// ..... // 赋值好了前 2 行(递归基), 其余的行就累加过去就好了 for row in 2..nrows { // 对于最后两行, 不需要启用 Selector if row < nrows - 2 { self.config.selector.enable(&mut region, row)?; } let c_cell = region.assign_advice( || "advice", self.config.advice, row, || a_cell.0.value().copied() + b_cell.0.value(), ).map(ACell)?; a_cell = b_cell; // let mut a_cell ... b_cell = c_cell; } Ok(b_cell) // return the last cell. } }
Test
如下 instance , 里面是 Public input
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { #[test] fn test_example2() { let k = 4; let a = Fp::from(1); // F[0] let b = Fp::from(1); // F[1] let out = Fp::from(55); // F[9] let circuit = MyCircuit(PhantomData); let mut public_input = vec![a, b, out]; let prover = MockProver::run(k, &circuit, vec![public_input.clone()]).unwrap(); prover.assert_satisfied(); public_input[2] += Fp::one(); let _prover = MockProver::run(k, &circuit, vec![public_input]).unwrap(); // uncomment the following line and the assert will fail // _prover.assert_satisfied(); } }
change k from 13 to 4, the line will be smaller so now you are not calim about the main function
- the MockProver will tell you constrains that
- the
pngwill tell you a constraintyou have ignored!
Usage
cargo test -- --nocapture fibonacci::example1
# Draw
cargo test --release --all-features plot_fibo1
- the white column is the instance column,
- the pink one is the advice and
- the purple one is the selector.
- the green part shows the cells that have been assigned
- light green : selector not used.
Reference :
—— 中文版本结束 ——
Example 2
Recap Table in Example-1 :

the problem we noticed like inside example-1 is that there are basically
- too many duplicate cells , so every time you need copy two cells from previous row to next row , not efficient
- better solution : Use rotation to access to the multiple rows.

在本例子中, 代码将更加紧凑和模块化, 以下是一些主要的区别 :
Advice Columns:
- ex 1 :
- 用了 3 个 advice columns:
col_a,col_b和col_c,这 3 个 columns 的第一行用来存储 Fibonacci 序列的连续的 3 个数 configure()在 3 个 advice columns 中为每一个需启用enable_equality,并为每一个都建立了门约束。
- 用了 3 个 advice columns:
- ex 2:
- 仅使用了一个 advice column,并依赖 rotation(轮转, 即 )来访问连续的数, 减少了各种复制
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { // example-1 pub fn configure( .., advice: [Column<Advice>; 3], .. { let col_i = advice[ii]; meta.enable_equality(col_i); // 很多列需要声明, 需要 enable... meta.create_gate("add", |meta| { let s = meta.query_selector(selector); let a = meta.query_advice(col_a, Rotation::cur()); //📢 let b = meta.query_advice(col_b, Rotation::cur()); //📢 let c = meta.query_advice(col_c, Rotation::cur()); //📢 } ---------------------------------------- // example-2 pub fn configure( .., advice: Column<Advice>, .. { meta.enable_equality(advice); //所有 advice 列只在此 enable once. meta.create_gate("add", |meta| { let s = meta.query_selector(selector); let a = meta.query_advice(advice, Rotation::cur()); //💡 let b = meta.query_advice(advice, Rotation::next());//💡 let c = meta.query_advice(advice, Rotation(2));} //💡 }
Rotation::cur()当前行Rotation::next()下一行Rotation(2)再下一行
The Polynomial Identity :
- 数据赋值:
- ex 1: 初始的 Fibonacci 数
a和b被赋值到两个不同的 advice columns,而他们的和则被赋值到第三个 column。 - ex 2: 所有的 Fibonacci 数都在同一个 advice column,但在不同的行 (thanks to rotation)
- ex 1: 初始的 Fibonacci 数
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { //// Example 2 //// pub fn assign(..., nrows){ layouter.assign_region("entire fibonacci table", |mut region| { // 为前两行启用 selector,这意味着我们将从 instance 列(可能是公共输入) // 中复制 Fibonacci 序列的前 2 个数字 self.config.selector.enable(&mut region, 0)?; self.config.selector.enable(&mut region, 1)?; // assign_advice_from_instance 方法,将 instance 列的前两个值 // (即 Fibonacci 序列的前两个数字)赋给 advice 列中的前两个单元格 // 后面在 MockProver 中, 我们会传入 instance 作为 Public input let mut a_cell = region.assign_advice_from_instance( || "1", self.config.instance, 0, self.config.advice, 0, // row )?; let mut b_cell = region.assign_advice_from_instance( || "1", self.config.instance, 1, // 这里写 0 也不报错, 写 1/2/3 就会报错了.. self.config.advice, 1, // row )?; // 赋值好了前 2 行(递归基) ,其余的行就累加过去就好了 for row in 2..nrows { if row < nrows - 2 { self.config.selector.enable(&mut region, row)?; } let c_cell = region.assign_advice( || "advice", self.config.advice, row, || a_cell.value().copied() + b_cell.value(), )?; a_cell = b_cell; b_cell = c_cell; } Ok(b_cell) } }
- 生成的 Fibonacci 数:
- Version 1: 使用方法
assign_row从前两个数生成下一个数。 - Version 2: 使用一个循环在整个 Fibonacci 表格中为所有的数赋值。
- Version 1: 使用方法
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { //// Example 2 //// pub fn assign(..., nrows){ // 赋值好了前 2 行(递归基) ,其余的行就累加过去就好了 for row in 2..nrows { if row < nrows - 2 { self.config.selector.enable(&mut region, row)?; } let c_cell = region.assign_advice( || "advice", self.config.advice, row, || a_cell.value().copied() + b_cell.value(), )?; a_cell = b_cell; b_cell = c_cell; } Ok(b_cell) } }
如下 instance , 里面是 Public input
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { #[test] fn test_example2() { let k = 4; let a = Fp::from(1); // F[0] let b = Fp::from(1); // F[1] let out = Fp::from(55); // F[9] let circuit = MyCircuit(PhantomData); let mut public_input = vec![a, b, out]; let prover = MockProver::run(k, &circuit, vec![public_input.clone()]).unwrap(); prover.assert_satisfied(); public_input[2] += Fp::one(); let _prover = MockProver::run(k, &circuit, vec![public_input]).unwrap(); // uncomment the following line and the assert will fail // _prover.assert_satisfied(); } }
- the white column is the instance column,
- the pink one is the advice and
- the purple one is the selector.
- the green part shows the cells that have been assigned
- light green : selector not used.
cargo test --all-features -- --nocapture print
change k from 13 to 4, the line will be more small so now you are not calim about the main function .
- the MockProver will tell you constrains that ,
- the
pngwill tell you a constraintyou have ignored!
Row & Column in Region
Compared example-1 with example-2 :
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { meta.create_gate("add", |meta| { // col_a | col_b | col_c | selector // a b c s let s = meta.query_selector(selector); let a = meta.query_advice(col_a, Rotation::cur()); let b = meta.query_advice(col_b, Rotation::cur()); let c = meta.query_advice(col_c, Rotation::cur()); vec![s * (a + b - c)] --------------------------------------------- meta.create_gate("add", |meta| { // advice | selector // a | s // b | // c | let s = meta.query_selector(selector); let a = meta.query_advice(advice, Rotation::cur()); let b = meta.query_advice(advice, Rotation::next()); let c = meta.query_advice(advice, Rotation(2)); vec![s * (a + b - c)] }
We see :
col_a / col_b / col_crepresent differentRotation::cur() / Rotation::next() / Rotation::prev() / Rotation(2)represent different
cargo test -- --nocapture fibonacci::example2
References :
- Jason Morton halo2 codes
- ZCash halo2 books
- trapdoor-tech halo2 book
- icemelon/HaiCheng Shen
- 0xPARC halo2